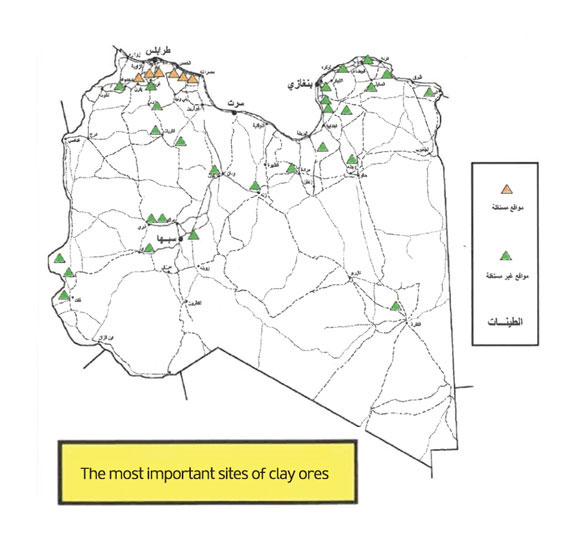
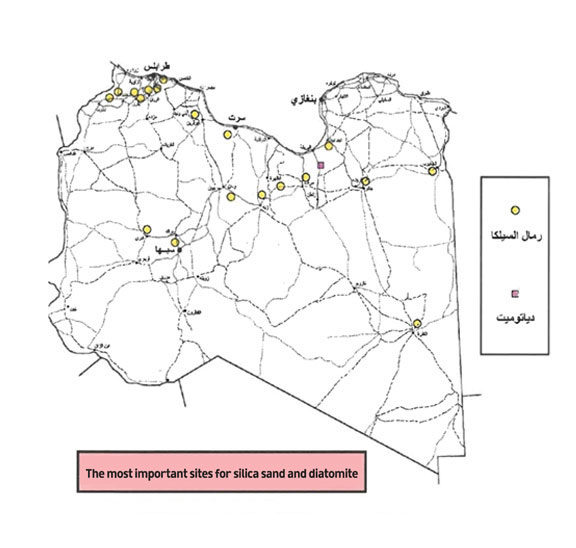
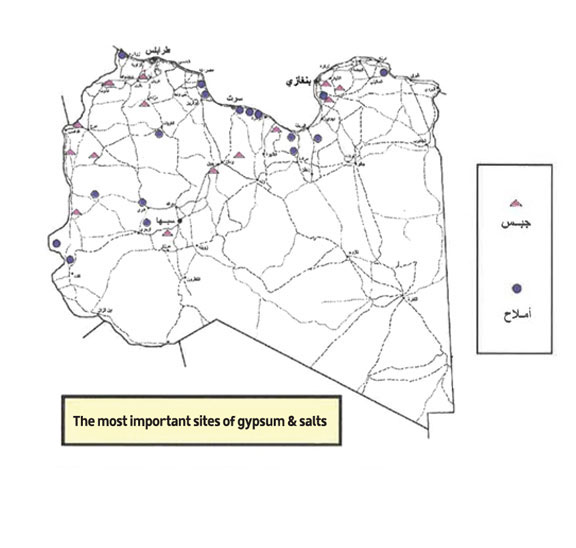
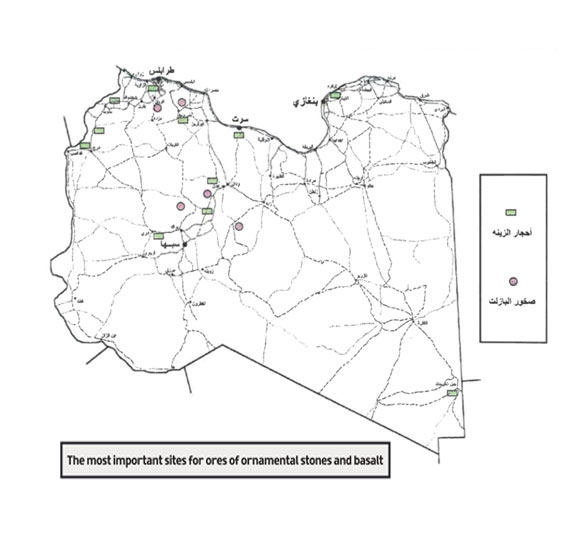
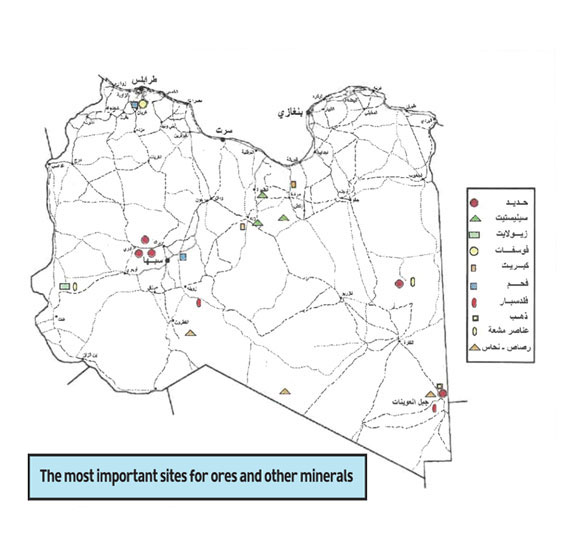
Carbonate Rocks
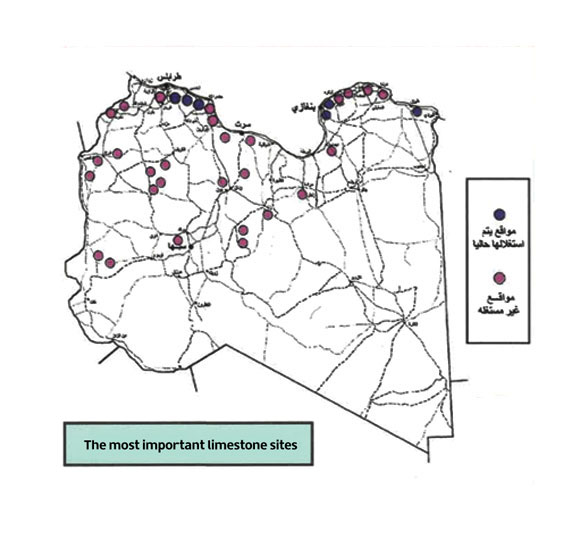
1. Limestones
It is a compound of calcium carbonate, which has many uses in the industrial and agricultural fields, as it is the basic material used in the cement and lime industries, as an auxiliary material in the iron and steel industry, and as a filler in many industries such as paint, plastics, and adhesives, in addition to its use in industries Chemical, and algebraic stones are widely spread in the Libyan state, especially in the northern regions, where many sites have been identified, and some of them have been studied in detail, as they are invested in many existing factories for the production of cement, algebra, iron, steel, glass, paint, and the plastics industry.

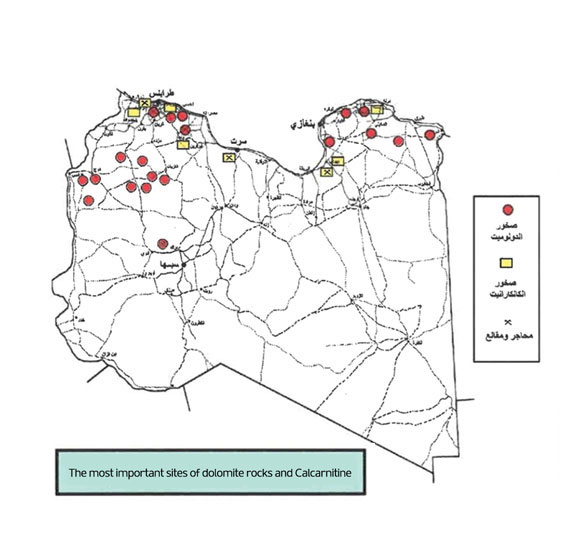
2. Dolomitic stones
It is one of the types of carbonate rocks resulting from the overlapping of calcium carbonate and magnesium carbonate in varying proportions, as the type of rock ranges from algebraic to dolomite, as the percentage of magnesium carbonate increases. Dolomite stones are used in many industrial purposes, especially in the manufacture of refractory bricks and the glass industry, and as a filler.
For the production of polished slides and aggregates, and dolomite stones are found in many locations in the Libyan state, where they are invested extensively in the production of shurchur and as an auxiliary material in the iron and steel complex and in many other industries.
For the production of polished slides and aggregates, and dolomite stones are found in many locations in the Libyan state, where they are invested extensively in the production of shurchur and as an auxiliary material in the iron and steel complex and in many other industries.
3. Calcarnet
It is one of the types of carbonate rocks of marine origin, resulting from the accumulation of seashells mixed with sand in varying proportions.
They are spread along the coastal strip, as they differ in their thickness, degrees of cohesion, and chemical components from one site to another, and due to their presence in the form of intersecting and brittle layers, they are used on a large scale It is widely used in the production of stone building blocks and is also used as a source of building sand, as its random and intensive exploitation in the northwestern regions resulted in many environmental problems that necessitate finding alternatives to the production of building bricks from other materials such as forced sand bricks, gypsum molds and light bricks.
They are spread along the coastal strip, as they differ in their thickness, degrees of cohesion, and chemical components from one site to another, and due to their presence in the form of intersecting and brittle layers, they are used on a large scale It is widely used in the production of stone building blocks and is also used as a source of building sand, as its random and intensive exploitation in the northwestern regions resulted in many environmental problems that necessitate finding alternatives to the production of building bricks from other materials such as forced sand bricks, gypsum molds and light bricks.